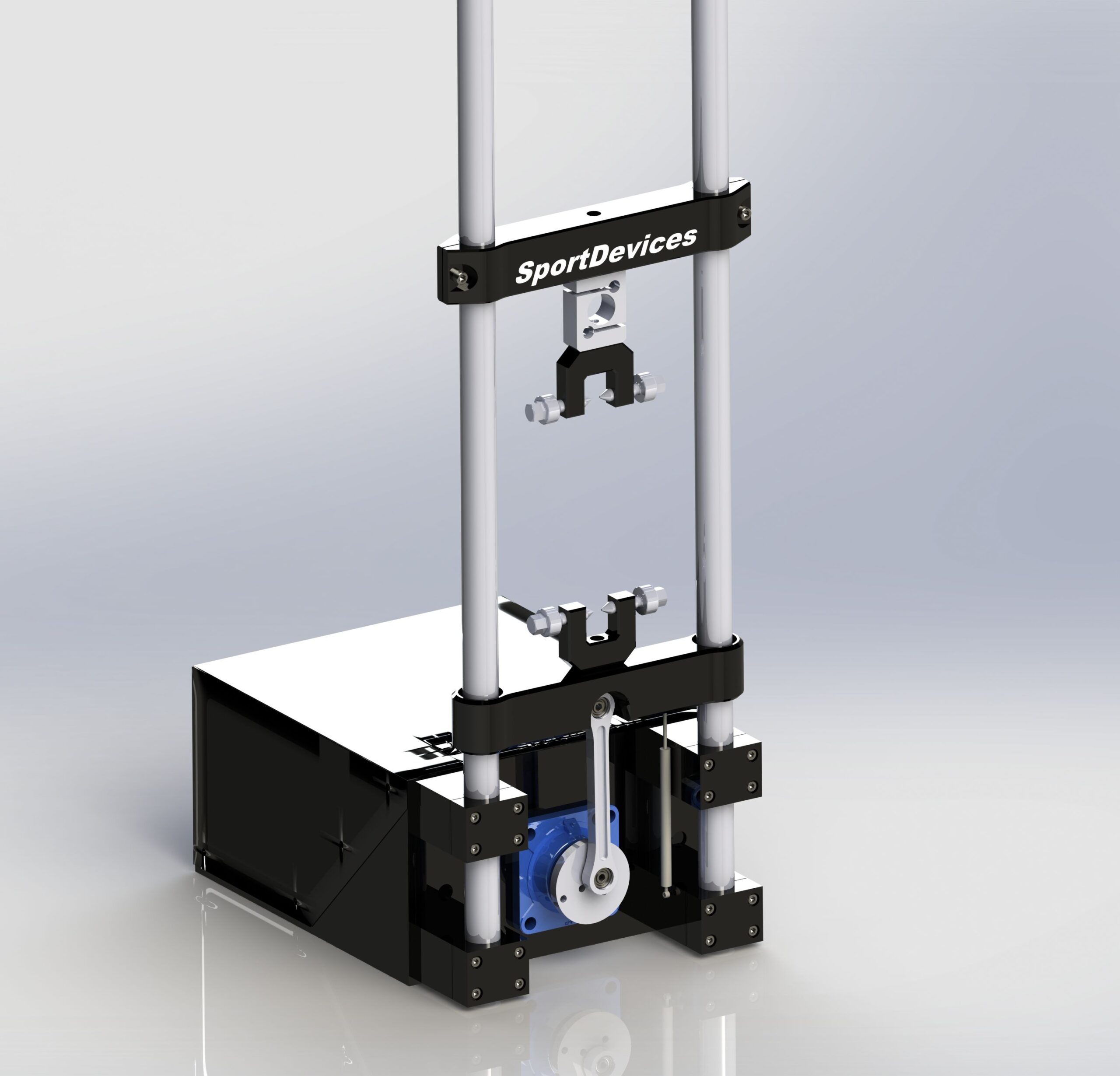
Specifications
Electric Motor
Shockabsorber dynamometers are usually powered by 3-phase AC induction electric motors. The motors size and power is limited to its supply voltage. It is strongly recommended to drive the motor with a VFD to be able to perform the automated multi-speed tests. For power values under 4 HP, the VFD can be powered from a single phase grid. But for higher power values, normally 3-phase grid is necessary.
Reduction Gearbox
Output from the motor is geared down with a reduction box. The maximum output shaft speed should be in the 300 to 500 RPM range.
Note that although most induction motors work at 1450 RPM at 50 Hz, the VFD can easilly increase this speed up to almost twice (100 Hz), which results in a high torque at low RPM (for 300 RPM reduction box), and increased speed to allow testing the shockabsorber at higher speeds with a small reduction in total power.
Load Cell
A load cell is a transducer that converts force on it into analog electrical signals. A load cell attached to the crossbeam will measure the force placed on the shock.
Shock temperature sensor
Shock temperature is measured using a thermocouple attached to the casing of the shock with a Velcro strap. Shock performance can vary dramatically at different temperatures. With the temperature monitoring system, you can determine how your shock will proform under various temperatures. You can warm the shock directly on dynamemeter (thermocouple is not included in the kit).
Potentiometer
Shockanalyzer DAQ uses a 100 mm potentiometer to meassure speed and position, this part is supplied with the kit. There is an optional 150 mm potentiometer.
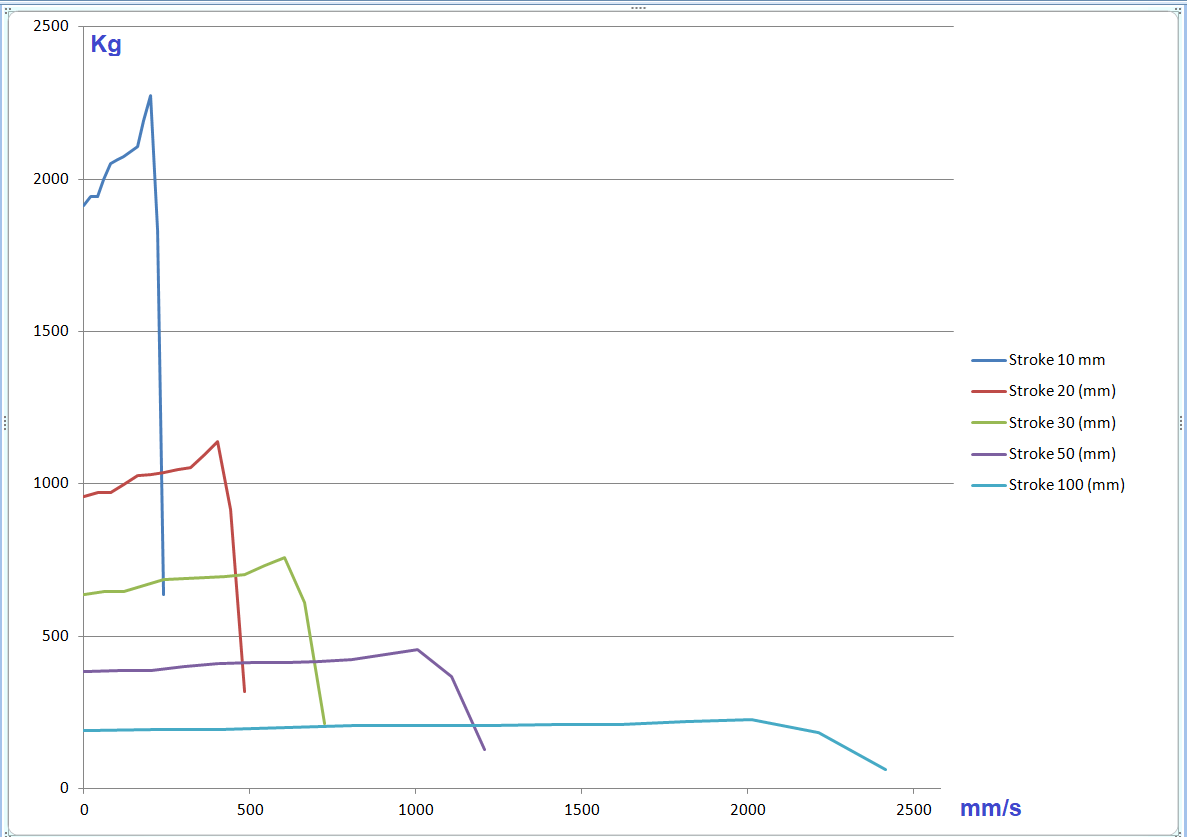
Force vs Speed at different Strokes